Traffic Recovery for Manya Group (Delhi) After a Major Google Update
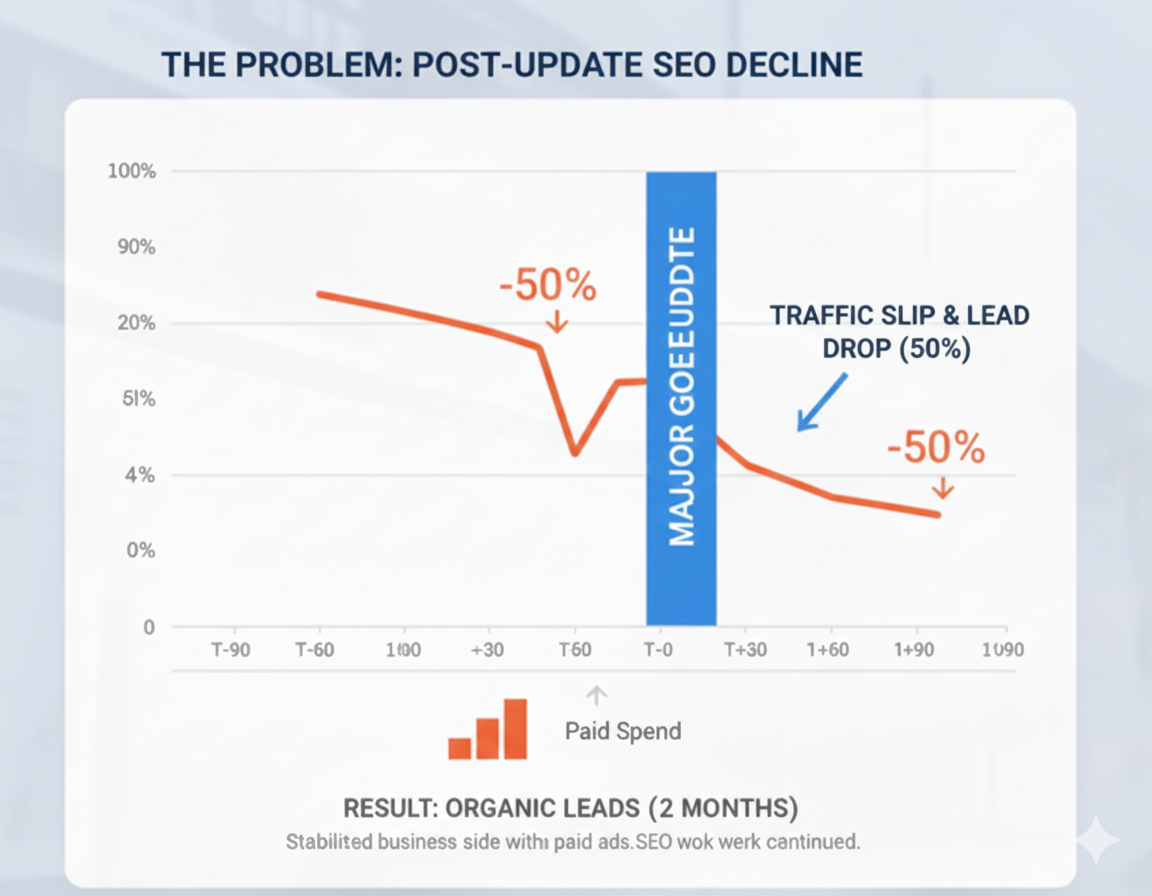
When Manya Group, a well-known multi-location EdTech organisation in Delhi, reached out, they were trying to understand a sudden and serious drop in performance. A major Google update had reduced their organic traffic by almost half, and the fall in traffic immediately showed up in their lead numbers.
To protect admissions, the team had increased paid spend, but this wasn’t something they wanted to depend on long term. They needed to understand what caused the decline, how much of it was recoverable, and how quickly they could get back to a stable position.
What Led to the Decline in Organic Traffic
The first step was to retrace the drop across GA, GSC, and Manya’s historical lead data from LeadSquared. The patterns showed two things clearly:
-
The Google update triggered the visible fall
-
But deeper issues had been building for a while
Some program and location pages lost visibility almost immediately after the update. Others had been weakening for months. This mix usually means the update didn’t create the problem, it simply exposed what was already slipping.
We found gaps in program content, outdated templates, inconsistent location signals, and clusters that didn’t fully match the way students search today. On top of that, conversion pathways weren’t aligned with where users were showing intent, so the traffic that remained wasn’t translating well into enquiries.
It wasn’t one issue. It was several small weaknesses that added up.
What Manya Group Needed in the Short and Long Term
Before moving into solutions, we clarified the goals with the leadership team:
Short-term:
Stop the decline in organic leads and stabilise enquiry flow without pushing paid budgets further.
Long-term:
Fix the structural issues so the site could regain visibility and stay steady during future Google updates.
Both needed to happen together. If they focused only on traffic recovery, lead volume would stay unpredictable. If they focused only on leads, the structural problems would return in the next update.
How We Structured the Recovery
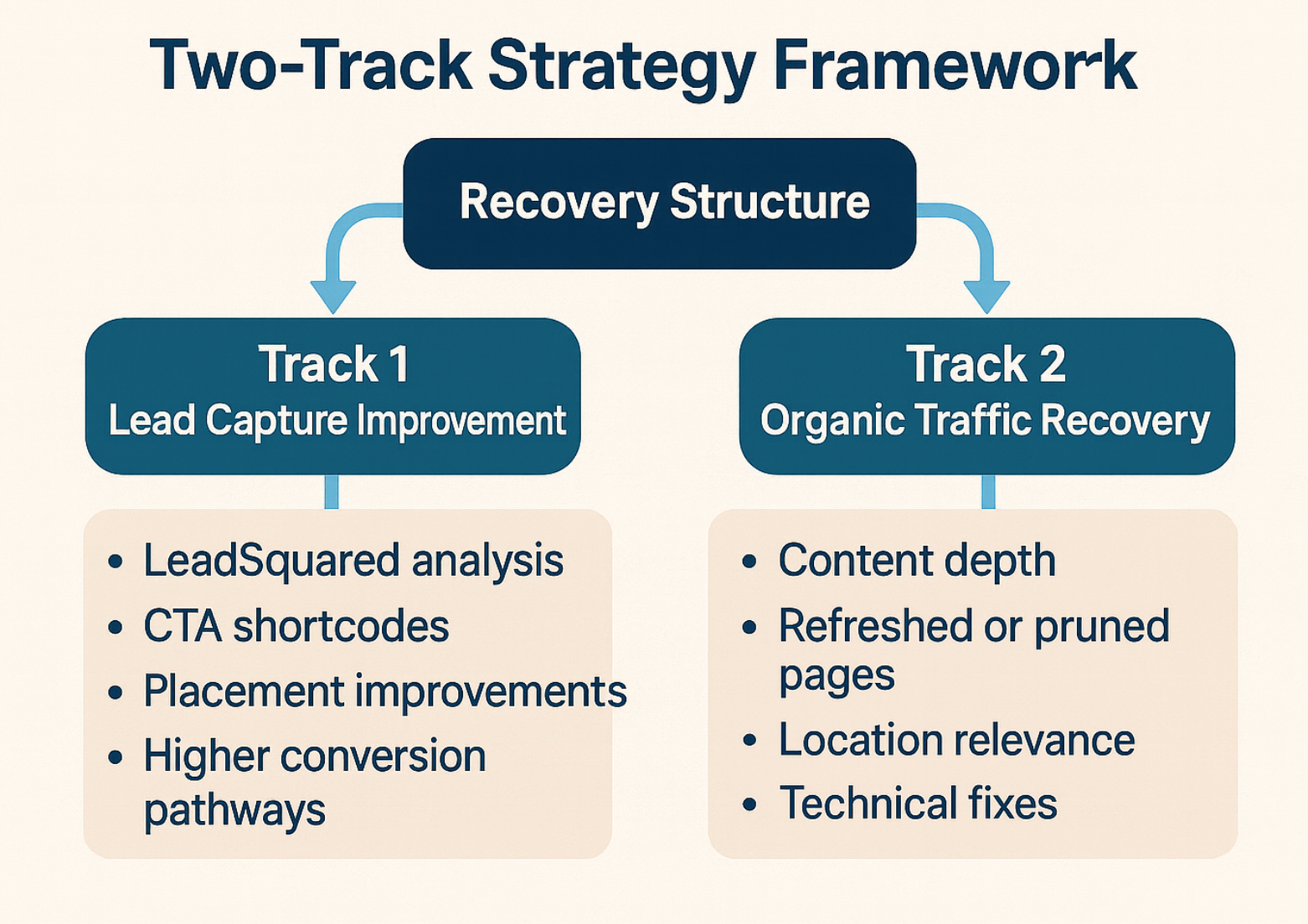
To keep things practical, we divided the work into two parallel tracks.
Track 1: Improving Leads From the Traffic They Still Had
We started with LeadSquared data because it gave the clearest picture of what had historically converted well—program categories, form placements, and the types of leads that usually turned into actual admissions.
A deeper look showed that users were landing on relevant pages but not finding strong or visible CTAs at the right moments. Several high-intent pages had enquiry prompts buried or inconsistent.
We created a set of CTA shortcodes that made it easy for the internal team to place enquiries, callbacks, and program-specific prompts exactly where users paused or scrolled the most.
These were implemented quickly, and within two months, organic leads improved by roughly 30 percent, even though traffic had not yet recovered.
This stabilised the business side while the rest of the SEO work moved forward.
Track 2: Repairing the Content and Structural Weaknesses
Once short-term stability was under control, we went deeper into the content and technical audit.
The Google update didn’t wipe out strong content; it exposed where the site no longer aligned with student search behaviour. We identified:
-
program pages that needed depth
-
missing subtopics and incomplete clusters
-
location pages that lacked consistent relevance
-
outdated templates that didn’t highlight key information
-
weak internal pathways that made it hard for Google to understand hierarchy
The recovery plan focused on strengthening these pieces step by step, starting with core program pages, then fixing location signals, and finally rebuilding internal linking and supporting content.
It wasn’t rushed. It was sequenced, because the site needed to show clear signals before Google would respond.
Early Signs of Recovery
By the third month, small but important improvements appeared. Google started crawling priority pages more frequently, queries that had disappeared showed impressions again, and rankings stopped fluctuating as widely.
These were early indicators that the structural work was taking hold.
When Recovery Became Meaningful Growth
By the fifth month, most of the traffic loss had been recovered. The real test came when Google rolled out the next update. This time, instead of dropping again, Manya Group’s improved structure helped them gain visibility across several program categories and key metro locations.
The site was now performing with more stability than it had before the original decline.
What This Case Shows About EdTech SEO
Manya Group’s situation is common in multi-location EdTech:
-
Small content and structure issues compound over time
-
Google updates expose the weaknesses all at once
-
Lead pathways matter as much as traffic
-
Using LeadSquared data helps fix conversion issues with clarity
-
Recovery works best when stabilisation and SEO repair run together
It wasn’t a quick fix. It was a structured recovery focused on depth, clarity, and making sure the site matched how students actually search today.
You may also like to read –
FAQs
Why did Manya Group lose so much traffic after the Google update?
The update didn’t create the problem on its own. It highlighted gaps in program depth, location relevance, and older templates that had weakened over time. When the update rolled out, those weaknesses became visible all at once.
How did LeadSquared data help during the recovery?
LeadSquared showed which enquiries historically converted best and where users dropped off. This allowed us to update CTAs, placements, and pathways in a way that immediately improved lead capture from the remaining traffic.
What were the short-term and long-term goals for the recovery?
Short-term, the focus was on stabilising enquiry volume without increasing paid spend. Long-term, the goal was to rebuild content, structure, and relevance so the site could regain lost visibility and stay resilient during future updates.
What were the most important fixes on the SEO side?
The combination of refreshed content, deeper program coverage, improved location signals, corrected internal pathways, and template updates created the foundation Google needed to re-evaluate the site.
How soon did Manya Group start seeing improvements?
Lead capture improved within the first two months. Organic recovery began around the third month, with most visibility restored by the fifth month and further gains appearing after the next Google update.
Can similar EdTech websites avoid this type of drop?
Yes. Sites with clear intent coverage, structured location signals, updated templates, and consistent internal linking are far more stable during Google updates. Addressing these areas early prevents sudden declines.


